By Edrees Team | Jul 3, 2017 | Featured, Dr. Hani Badhaddah, Articles | 0 comments
Riyadh, July 25, 2019 – Manal Al-Ja’eed
Dr. Hani Badhaddah, an American Board-Certified specialist in Foot and Ankle Medicine and Surgery, discussed the increased susceptibility of diabetic patients to Charcot foot. This condition is prevalent among individuals with diabetes due to their tendency to lose sensation in their feet and experience nerve damage. Dr. Badhaddah noted that 25% of Charcot foot cases necessitate surgical intervention.
Understanding Charcot Foot
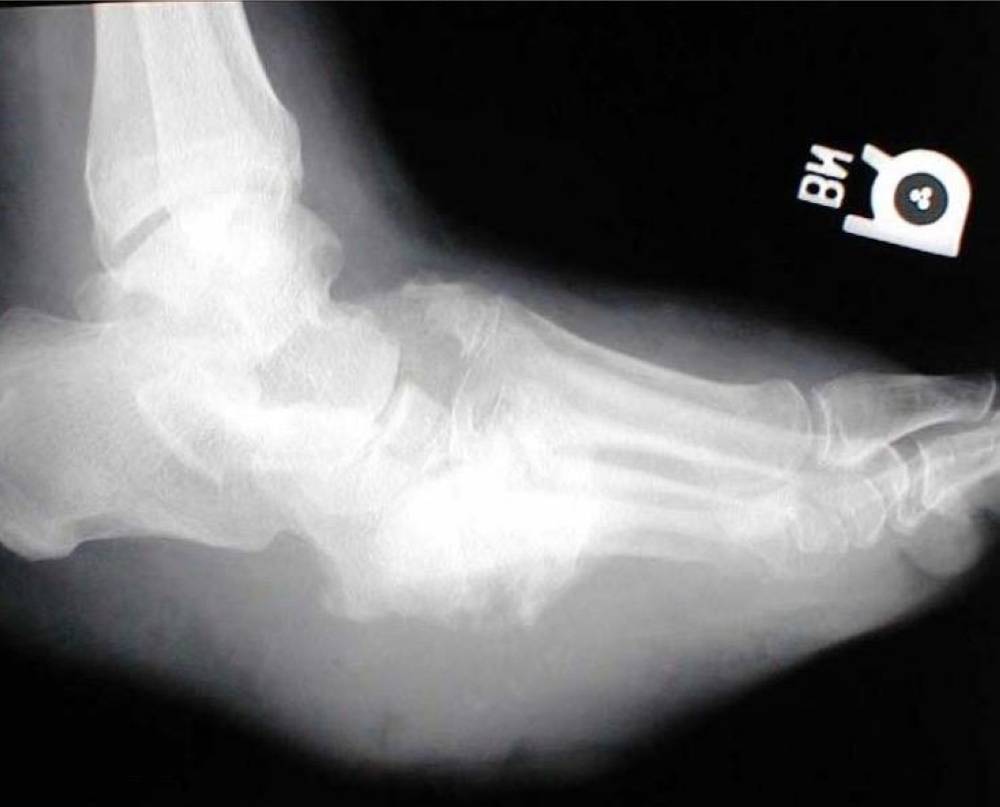
Charcot foot, also referred to as diabetic foot fractures, affects individuals with peripheral neuropathy and a loss of sensation. This condition weakens the bones, making them more prone to fractures. It is distinct from fractures caused by injuries or accidents and is named after the French physician who first identified it.
Foot Shape and Symptoms
Dr. Badhaddah explained that Charcot foot or diabetic foot fractures often follow an injury such as twisting the ankle or placing unusual stress on the feet, such as walking long distances. Symptoms include increased foot temperature, swelling, and redness. Patients might also experience foot pain, but due to the loss of sensation, they may continue to walk on the affected foot, which can lead to multiple fractures and changes in foot shape.
Challenges in Diagnosis
Early-stage Charcot foot can resemble other conditions like venous thrombosis, cellulitis, gout, or osteomyelitis, making it difficult to diagnose. X-rays may initially show no fractures, complicating the diagnosis for non-specialists. Dr. Badhaddah emphasized that early diagnosis is crucial to minimize complications and the need for surgical intervention. Therefore, diabetic patients who notice symptoms should consult a foot and ankle specialist promptly.
Treatment Approaches
Currently, there are no medications or injections specifically for treating Charcot foot. The primary treatment involves avoiding walking on the affected foot and applying a cast. This cast is initially changed after one week and then every two weeks for a total of three months. X-rays are taken at each interval to monitor progress. After three months, the foot is placed in a specialized medical boot designed for Charcot foot for an additional three months. At the end of this period, the condition is re-evaluated to decide if further non-surgical treatment or surgical intervention is necessary. Dr. Badhaddah highlighted that 25% of Charcot foot cases require surgery.
Preventive Measures
To prevent Charcot foot, Dr. Badhaddah advised maintaining blood sugar levels, regular follow-ups with a diabetes specialist, daily foot inspections, choosing appropriate footwear, avoiding strenuous physical activities, and seeking immediate medical attention if any foot symptoms arise.
Causes and Symptoms of Charcot Foot
- Causes: Peripheral neuropathy, loss of muscle support, loss of foot sensation and pressure regulation, and increased blood flow due to small blood vessel dysfunction.
- Initial Signs and Symptoms: Redness, warmth upon touch, and swelling of the foot.
Treatment Methods
- Avoid walking on the affected foot and apply a cast.
- Change the cast initially after one week and then every two weeks for three months.
- After three months, use a specialized medical boot designed for Charcot foot for another three months.
- Reevaluate the condition to determine if further non-surgical or surgical treatment is required.
For more details, visit the article on Al-Watan newspaper’s website.